Biofuel is a collective name for fuels made from biomass. Biodiesel is the most well-known liquid fuel for transport, but there is also bioethanol, biogas and bio-butanol. This website mainly contains information about biodiesel.
Biodiesel is an alternative to fossil diesel. Biodiesel is mainly used by mixing it in ‘ordinary’ fossil diesel. The European Union has decided that 14 percent of road traffic in Europe must use renewable energy by 2030. B7 is then refueled at the pump. The main reason for this compulsory blending is the contribution to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
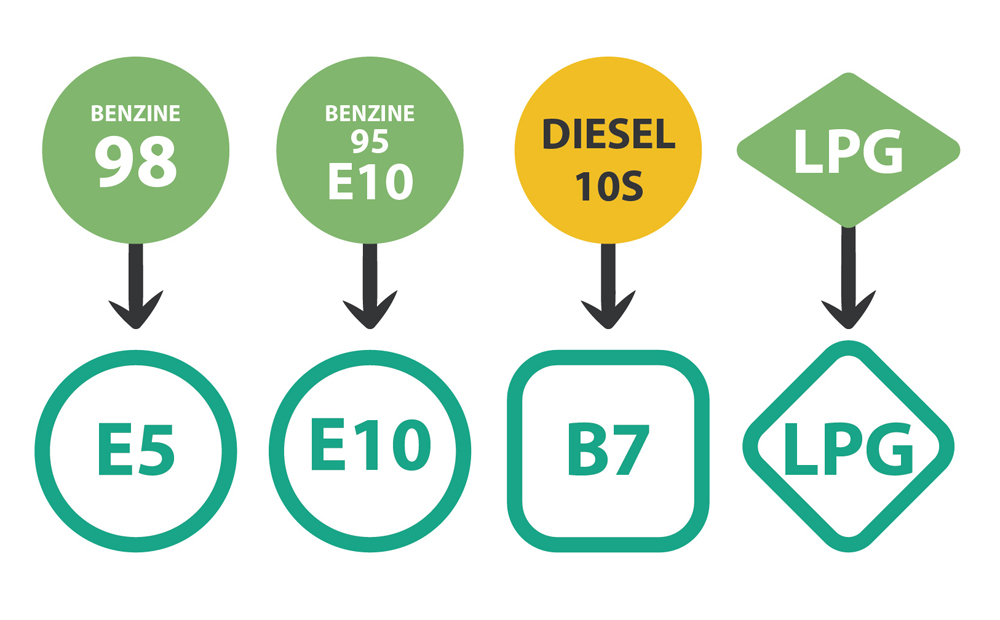
Since October 12, 2018, the logos for fuel at pumps are the same throughout Europe. The letter stands for the type of fuel: E is bioethanol, B is biodiesel and LPG is Liquefied Petroleum Gas. The figure represents the share of biofuel, 5, 10 and 7 percent respectively. There are different types of biodiesel. It is technically possible to run on 100% biofuel. But currently biofuels are blended with fossil fuels.
To fully understand what biodiesel is and why biodiesel is a sustainable alternative to fossil diesel, it is important to know how biofuel is made. Biodiesel is made from types of vegetable or animal oils and fats or from residues. The production of biodiesel can be divided into three categories. For example, biodiesel is made from: vegetable oil, animal fat and waste products such as used frying fat, fat from sewage and fat from the waste water from palm oil mills.
For the production of biodiesel, all raw materials must meet sustainability requirements set by the European Union. These sustainability requirements are checked by independent experts.